EMPOWERMENT TECHNOLOGIES
EMPOWERMENT TECHNOLOGIES
Prepared by:
ROMMEL M. MAGCALAS
Teacher II
Pagalanggang National High School
CONTENTSLesson 1: ICT and Its Current StateWhat is ICT?Current State of ICTWorld Wide Web (WWW) vs InternetWeb VersionsLesson 2: Online systems, functions, and platformsSix types of Social MediaDifferent Types of Online PlatformsLesson 3: NetiquettesWhat is Netiquettes?Core Rules of NetiquetteLesson 4: Online Safety and SecurityTips to stay safe onlineInternet-based threatsProtecting Reputations OnlineCopyright InfringementLesson 5: Online NavigationOnline NavigationSteps in Online NavigationResearch SkillsLesson 6: Applied Productivity Tools using Word ProcessorWord ProcessorWord Processor – Brief HistoryMicrosoft Word Brief HistoryMicrosoft Word Parts and UsesLESSON 7: Advanced Word Processing SkillsMail Merge and Label GenerationTwo Components of Mail MergeIntegrating Images and External MaterialsKinds of MaterialsImage PlacementLESSON 8: Advanced Spreadsheet SkillsWhat is a Spreadsheet Software?Key Terms in MS ExcelBASIC MATH OPERATIONSOTHER FUNCTIONSLESSON 9: Advanced Presentation SkillsPowerpointCreating an Effective PresentationLesson 10: Imaging and Design for Online EnvironmentTopic 1. Basic principles of graphics and layoutTopic 2. Creating infographicsTopic 3. Online file formats for imagesTopic 4. Uploading, sharing and image hostingLesson 11: Online Platforms for ICT Content DevelopmentTwo Types of PlatformsLesson 12: Basic Web Page CreationCreating a website using Microsoft WordLesson 13. Collaborative ICT DevelopmentOnline Collaborative ToolsLesson 14. Interactive MultimediaMultimedia ContentLesson 15. ICT as Platform for ChangeWhat is Advocacy?The Power of Social MediaWhat Is Digital Citizenship?What is the Digital Divide?The Role of ICT in Recent HistoryLesson 16. ICT Project for Social ChangeSocial ChangeSimplified ICT Project Process Overview:Creating a Concept PaperFive elements of a concept paperLesson 17: ICT Project Publication and StatisticsLesson 18: ICT Project MaintenanceUser FeedbackGoogle FormsLesson 19: The Disadvantage of ICTCybercrimesCombatting CybercrimesReferences
What is ICT?
Information Communication Technology (ICT) is an umbrella term referring to communication hardware or software that allows the access, storage, transmission and manipulation of information.
In terms of Hardware, ICT specifically encompasses radio, television, communication devices (smart and non-smart phones), desktops computers, laptops and network hardware and technologies.
ICT is also comprised of software, applications and platforms that allows information to be accessed, stored, transmitted and manipulated.
Current State of ICT
ICT is following certain trends as it is developing in this time and age. This trend dictates the idea and design of how ICT delivers information to people.
The following are emerging technologies, principles or concepts in ICT.
1. Convergent Technologies
This is when multiple different devices combine into a single gadget because of technological advancement.
One example of this is smartphone, where it is capable of doing the functions of a television, radio, computer, telephone, camera and GPS as a single device.
2. Social Media
These are software, applications or platforms that allow users to communicate in an online social communities or network.
Social media allows people to communicate faster through a larger number of people.
3. Mobile Technologies
This is a term for devices that are easily carried and allows fast means of communication.
These devices from the past were originally big and bulk, but due to the technological advancement, they become smaller and more compact.
World Wide Web (WWW) vs Internet
The Internet by definition is the actual interconnection of computers and other networks, while the web refers to the system that enables people to access information over the internet.
The internet is the hardware aspect because it relates to computer networks, connections and infrastructures.
The web on the other hand, refers to the software aspect as it relates to the Protocols or HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol).
HTTP are the system or procedures that enables the transfer of information in the internet web services, applications and platforms.
Web Versions
The web has three distinctive versions namely: Web 1.0, Web 2.0 and Web 3.0.
Some people think that the indicated web versions are updates across a particular point of history. The versions of the web are categorized based on functionality and features that it represents.
WEB 1.0
first generation of the evolution of web technologies.
The first commercial Web1 applications emerged in the early 1990s. At that time, "the Internet" consisted of static web pages. Static web pages consist of only text and images.
According to the inventor of the world wide web, Tim Berner Lee, web 1.0 is “Read only web” which means the user can only read whatever online content the creator has made.
WEB 2.0
second generation of the evolution of web technologies.
The term "Web 2.0" was coined by Darcy DiNucci.
Web 2.0 is “Read-Write”, which refers for the ability of the user to add content thru posting, sharing, commenting or rating.
Web 2.0 allows interaction not only in between the user and the creator but also to other users.
A Dynamic web page means displaying the different content with the same layouts and designs at each time. The best example for web 2.0 is Twitter, Facebook, and other similar social media sites which show different content for different users at the same time.
WEB 3.0
third generation of the evolution of web technologies.
Web 3.0 is a concept of how the web will evolve.
It provides a data-driven Semantic Web employing a machine-based understanding of data with the objective of developing a more intelligent and connected web experience for users.
Web 3.0 is not yet fully realized and is still developing, the full concept can still change.
Lesson 2: Online systems, functions, and platforms
1. Social Networks – These are sites that allows you to connect with other people with the same interests or background. Once the user creates his/her account, he/she can set up a profile, add people, share content, etc
Example: Facebook and Google+
2. Bookmarking Sites – Sites that allow you to store and manage links to various website and resources. Most of the sites allow you to create a tag to others.
Example: Pinterest
3. Social News – Sites that allow users to post their own news items or links to other news sources. The users can also comment on the post and comments may also be rank.
Example: Reddit and Digg
4. Media Sharing – sites that allow you to upload and share media content like images, music and video.
Example: Flickr, YouTube and Instagram
5. Microblogging – focus on short updates from the user. Those that subscribed to the user will be able to receive these updates.
Example: Twitter and Plurk, Tiktok
6. Blogs and Forums – allow user to post their content. Other users are able to comment on the said topic.
Example: Blogger, WordPress and Tumblr
Different Types of Online Platforms
1. WEB SEARCH ENGINES
It is a software system designed to search for information on the World Wide Web (WWW).
The search results are generally presented in a line of results referred to as Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs).
2. Communication Services
These are outsourced enterprise communications solutions that can be leased from a single vendor or provider.
A Communications Service Provider (CSP) is a provider that transports information electronically and can encompass public and private companies in telecom, internet, cable, satellite, and managed services business.
3. Payment System
It is any system used to settle financial transactions through the transfer of monetary value and includes institutions, instruments, people, rules, procedures, standards, and technologies.
With the advent of technology, these types of payments are now being done through online transactions. It has made payments and sending or receiving money more comfortable, convenient, less hassle, and not time-consuming for people.
Payment transactions are useful in many ways. These are:
1. Cash (bills and change) - It is one of the most useful ways to use for any purchase.
2. Personal checks (US check) - It is ordered through one's account.
3. Debit Card - When using this, the buyer takes the money directly out of his account.
4. Social Media
Social Media are forms of electronic communication through which users create online communities to share information, ideas, personal messages, and other content (as videos).
Social Media is a platform for broadcasting information.
Social media is a communication channel
5. Social Networking
Social Networking is a platform for communicating with one another.
Social Networking communication has a two-way nature.
6. PLATFORM FOR ADVERTISING
Facebook advertising is picking up speed in the business world.
They help make sure your advertising budget is not wasted on those who are not interested in what you are offering.
Facebook makes your product or service put into the hands of the exact person who wants it.
Online Advertising Platforms
Google Ads
Bing Ads
Facebook Ads
Instagram Ads
Twitter Ads
LinkedIn Ads
Pinterest Ads
Amazon Ads
7. PLATFORM FOR HASHTAGGING
Hashtags were first widely used on Twitter, but they have become commonplace on other social media platforms including Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Pinterest, and TikTok.
One hashtag is all it takes to launch your tweet’s success. A tweet that contains one hashtag will achieve an averaging of 90 interactions, according to TrackMaven. Tweets with more than one hashtag see a decline in engagement.
Use location-specific hashtags to increase reach/engagement. If engagement with an event is high enough, Twitter’s algorithm may identify this topic as trending for the specific geographic location. By implementing a geographic hashtag, companies can increase brand/event awareness when followers engage with the hashtag.
8. PLATFORM FOR GROUPING
LinkedIn is different from the rest of the social media outlets because it is specially designed for businesses and professionals.
Users mainly go to LinkedIn to showcase their job experience and professional thoughts, making it one of the most important platforms to use for those in B2B(business-to-business).
LinkedIn is a valuable tool not only for driving traffic but prospecting, establishing thought leadership, as well as recruiting.
9. PLATFORM FOR TEACHING
YouTube is the leading video-sharing platform in the world.
On your channel, your brand can share and edit videos, create playlists, and prompt discussions.
QUIZ#1
Lesson 3: Netiquettes
What is Netiquettes?
In this generation, people are dependent on the Internet. Like how people socialize face to face, we should follow etiquette at all times as it mirrors our personality. Being on different platforms, we should be aware of our actions and protect ourselves at the same time. Remember that once something has been shared online, it cannot be deleted.
Core Rules of Netiquette
Netiquette, or network etiquette, is concerned with the "proper" manner of communication in the online environment. Whenever you communicate in the virtual world, consider the following "rules," adapted from Virginia Shea's Core Rules of Netiquette.
Rule 1: Remember the Human
When communicating electronically, whether through email, instant message, discussion post, text, or another method, practice the Golden Rule: Do unto others as you would have others do unto you. Remember, your written words are read by real people, all deserving of respectful communication. Before you press "send" or "submit," ask yourself, "Would I be okay with this if someone else had written it?"
Rule 2: Adhere to the same standards of behavior online that you follow in real life
While it can be argued that standards of behavior may be different in the virtual world, they certainly should not be lower. You should do your best to act within the laws and ethical manners of society whenever you inhabit "cyberspace." Would you behave rudely to someone face-to-face? On most occasions, no. Neither should you behave this way in the virtual world.
Rule 3: Know where you are in cyberspace
"Netiquette varies from domain to domain." (Shea, 1994) Depending on where you are in the virtual world, the same written communication can be acceptable in one area, where it might be considered inappropriate in another. What you text to a friend may not be appropriate in an email to a classmate or colleague. Can you think of another example?
Rule 4: Respect other people's time and bandwidth
Electronic communication takes time: time to read and time in which to respond. Most people today lead busy lives, just like you do, and don't have time to read or respond to frivolous emails or discussion posts. As a virtual world communicator, it is your responsibility to make sure that the time spent reading your words isn't wasted. Make your written communication meaningful and to the point, without extraneous text or superfluous graphics or attachments that may take forever to download.
Rule 5: Make yourself look good online
One of the virtual world's best things is the lack of judgment associated with your physical appearance, the sound of your voice, or the clothes you wear (unless you post a video of yourself singing Karaoke in a clown outfit.) The quality of your writing will judge you, so keep the following tips in mind:
Always check for spelling and grammar errors.
Know what you're talking about and state it clearly.
Be pleasant and polite.
Rule 6: Share expert knowledge
The Internet offers its users many benefits; one is the ease in which information can be shared or accessed, and in fact, this "information sharing" capability is one of the reasons the Internet was founded. So in the spirit of the Internet's "founding fathers," share what you know! When you post a question and receive intelligent answers, share the results with others. Are you an expert at something? Post resources and references for your subject matter. You have recently expanded your knowledge about a subject that might be of interest to others? Share that as well.
Rule 7: Help keep flame wars under control
What is meant by "flaming" and "flame wars?" "Flaming is what people do when they express a strongly held opinion without holding back any emotion." (Shea, 1994). As an example, think of the kinds of passionate comments you might read on a sports blog. While "flaming" is not necessarily forbidden in virtual communication, "flame wars," when two or three people exchange angry posts between one another, must be controlled, or the camaraderie of the group could be compromised. Don't feed the flames; extinguish them by guiding the discussion back to a more productive direction.
Rule 8: Respect other people's privacy
Depending on what you are reading in the virtual world, be it an online class discussion forum, Facebook page, or an email, you may be exposed to some private or personal information that needs to be handled with care. Perhaps someone is sharing some medical news about a loved one or discussing a situation at work. What do you think would happen if this information "got into the wrong hands?" Embarrassment? Hurt feelings? Loss of a job? Just as you expect others to respect your privacy, so should you respect the privacy of others. Be sure to err on the side of caution when deciding to discuss or not to discuss virtual communication.
Rule 9: Don't abuse your power
Like in face-to-face situations, there are people in cyberspace who have more "power" than others. They have more expertise in technology or have years of experience in a particular skill or subject matter. Maybe it is you who possesses all of this knowledge and power! Just remember: knowing more than others do or having more power than others may have does not give you the right to take advantage of anyone. Think of Rule 1: Remember the human.
Rule 10: Be forgiving of other people's mistakes
Not everyone has the same amount of experience working in the virtual world. And not everyone knows the rules of Netiquette. At some point, you will see a stupid question, read an unnecessarily long response, or encounter misspelled words; when this happens, practice kindness and forgiveness as you would hope someone would do if you had committed the same offense. If it's a minor "offense," you might want to let it slide. If you feel compelled to respond to a mistake, do so in a private email rather than a public forum.
Lesson 4: Online Safety and Security
The internet is defined as the information highway.
This means that anyone has access to this highway, can place information, and can grab that information.
Any information, even things that you have set privately, can be accessed one way or another.
This is why social media networking sites like Facebook continue to improve their security features.
Tips to stay safe online
The Internet is a public place and it is up to you to protect yourself. Here are some tips to help you stay safe when using the Internet.
1. Be mindful of what you share online and what site you share it to.
2. Do not just accept terms and conditions; read it.
3. Check out the privacy policy page of a website to learn how the website handles the information you share.
4. Know the security features of the social networking site you use. By keeping your profile private, search engines will not be able to scan your profile.
5. Do not share your password with anyone.
6. Avoid logging in to public networks/Wi-Fi. Browsing in "incognito (or private) mode," a feature of the browser, will not protect you from hackers.
7. Do not talk to strangers whether online or face-to-face.
8. Never post anything about a future vacation. It is similar to posting, "Rob my house at this date."
9. Add friends you know in real life.
10. Avoid visiting untrusted websites.
11. Install and update an antivirus software on your computer. Use only one anti-virus software to avoid conflicts.
12. If you have a Wi-Fi at home, make it a private network by adding a password.
13. Avoid downloading anything from untrusted websites. You are most in peer-to-peer downloads (torrents) as the download is most likely not monitored by the site owner.
14. Buy the software; do not use pirated ones.
15. Do not reply or click links from suspicious emails.
Internet Threats
Internet-based threats expose people and computer systems to harm online. A broad scope of dangers fits into this category, including well-known threats like phishing and computer viruses.
Here are some of the threats you should be aware of when using the Internet:
1. Malware - stands for malicious software.
a. Virus - a malicious program designed to replicate itself and transfer from one computer to another either through the Internet and local networks or data storage like flash drives and CDs.
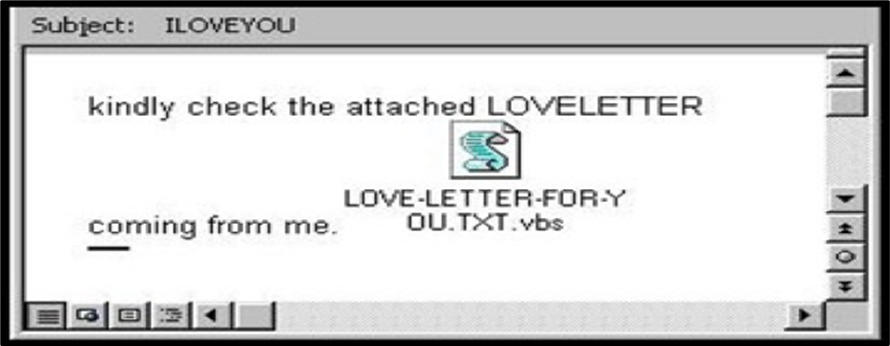
b. Worm - a malicious program that transfers from one computer to another by any type of means. Often, it uses a computer network to spread itself. For example, the ILOVEYOU worm (Love Bug Worm) created by a Filipino.
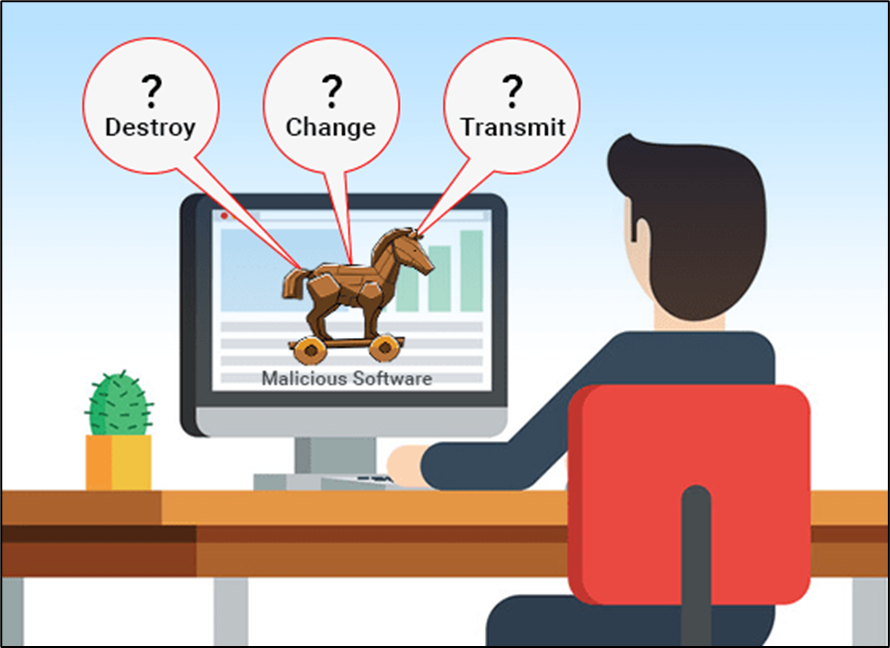
c. Trojan - a malicious program that is disguised as a useful program but once downloaded or installed, leaves your PC unprotected and allows hackers to get your information.
*Rogue security software — tricks the user into posing that it is a security software. It asks the user to pay to improve his/her security but in reality, they are not protected at all.
d. Spyware — a program that runs in the background without you knowing it (thus called "spy"). It has the ability to monitor what you are currently doing and typing through keylogging.
*Keyloggers — used to record the keystroke done by the users. This is done to steal their password or any other sensitive information. It can record email, messages, or any information you type using your keyboard.
e. Adware — a program designed to send you advertisements, mostly as pop-ups.
2. Spam — unwanted email mostly from bots or advertisers. It can be used to send malware.
3. Phishing - Its goal is to acquire sensitive personal information like passwords and credit card details. This is done by sending you an email that will direct the user to visit a website and be asked to update his/her username, password, credit card, or personal information.
*Pharming - a more complicated way of phishing where it exploits the DNS (Domain Name Service) system. Redirects internet users to fake websites to steal personal or financial information.
Protecting Reputations Online
In the past, doing something embarrassing was not much of a big deal. It happened; people would laugh at it, and they would move on. Nowadays, embarrassing moments are captured using any device you could imagine. What is worse is that people can easily upload it to the Internet, where it can be stored forever. This could impact not only your reputation but also the people around you. What is worse is that people tend to ignore this fact and suffer from it later in their life.
Once you post something over the Internet, search engines keep them in their archives for search results. This makes anything you post to last forever even if you delete it in your page. Something you and your friends find funny today may be something that could harm someone's reputation later.
Before hiring, companies do a background check on the applicant, and the easiest way to check your background is to visit pages that are related to you. Thus, if they find disreputable information about you, it may harm your reputation even if this information has been discarded.
Think Before You Click
Here are things you might want to consider before posting something over the Internet:
1. Before you post something on the web, ask these questions to yourself: Would you want your parents or grandparents to see it? Would you want your future boss to see it? Once you post something on the web, you have no control of who sees your posts.
2. Your friends depend on you to protect their reputation online. Talk to your friends about this serious responsibility.
3. Set your post to "private." In this way, search engines will not be able to scan that post.
4. Avoid using names. Names are easy for search engines to scan.
5. If you feel that a post can affect you or other's reputation, ask the one who posted it to pull it down or report it as inappropriate.
Copyright Infringement
If you create something - an idea, an invention, a form of literary work, or a research, you have the right as to how it should be used by others. This is called intellectual property. In other words, the copyright law includes your rights over your work, and anyone who uses it without your consent is punishable by law. Try grabbing any book then browse its first few pages and you will find a page with a disclaimer with the words: "No part of this book may be copied, reproduced..." That is a copyright page.
Here are some tips that could help you avoid copyright infringement:
1. Understand. Copyright protects literary works, photographs, paintings, drawings, films, music (and lyrics), choreography, and sculptures, but it generally does NOT protect underlying ideas and facts. This means that you can express something using your own words, but you should give credit to the source.
2. Be responsible. Even if a material does not say that it is copyrighted, it is not a valid defense against copyright. Be responsible enough to know if something has a copyright.
3. Be creative. Ask yourself whether what you are making is something that came from you or something made from somebody else's creativity. It is important to add your own creative genius in everything that will be credited to you.
4. Know the law. There are some limitations to copyright laws. For instance in the Philippines, copyrights only last a lifetime (of the author) plus 50 years. There are also provisions for “fair use" which mean that an intellectual property may be used without a consent as long as it is used in commentaries, criticisms, search engines, parodies, news reports, research, library archiving, teaching, and education. If you have doubts that what you are doing does not fall under the policy of fair use, seek permission first. Another misconception is that fanfiction (Wattpad) is not copyright infringement. In reality, it is and some copyright holders ignore them but they can optional use their rights.
QUIZ#2
Lesson 5: Online Navigation
Online Navigation
The manner of collectively searching for and saving requested information through the computer from databanks that are online
It is an attempt to be more precise in providing information based on a certain word.
Search Engines
These are software systems that are designed to search for information on the World Wide Web.
Examples of Search Engines
Baidu
Bing
Yahoo
DuckDuckGo
Steps in Online Navigation
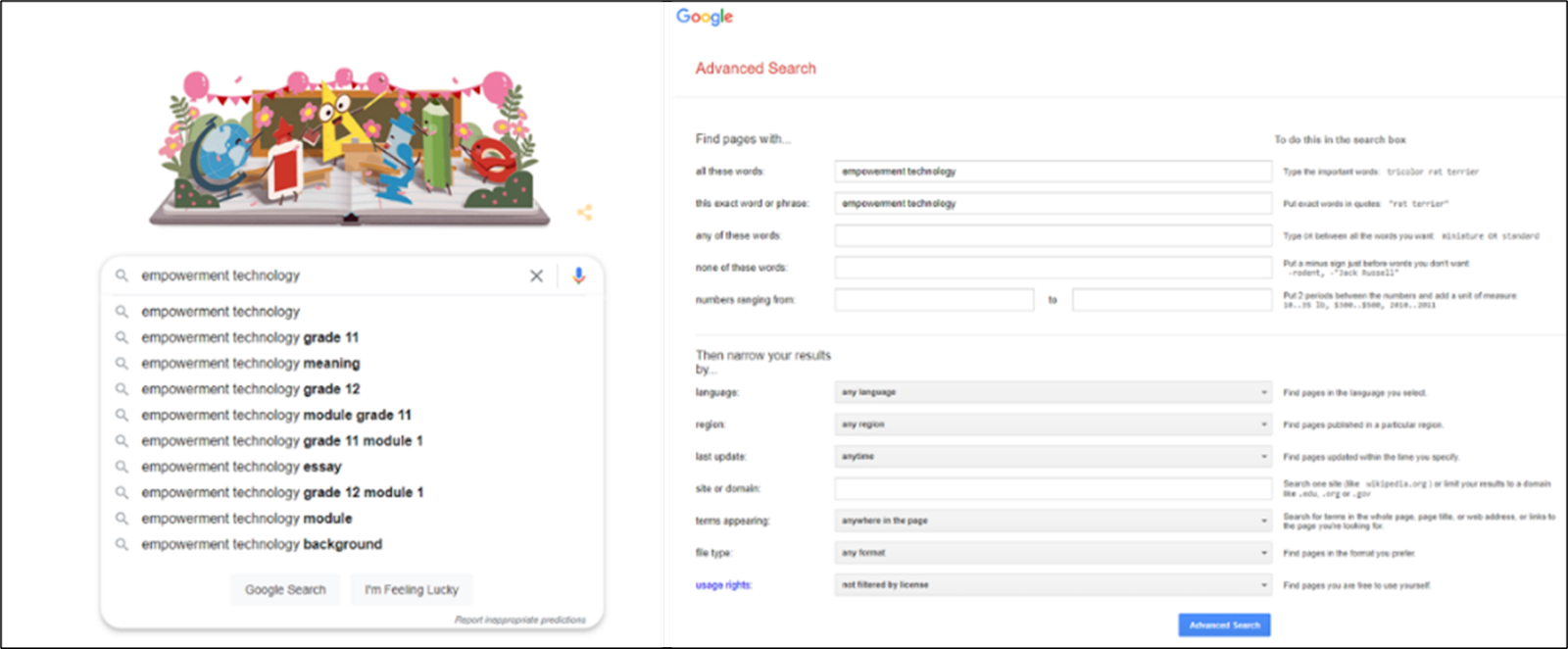
1. In your desktop, laptop or smartphones, open the browser and search Google and type the word, phrase or thought you want to search.
2. On the right part of the window, click setting and the google search settings pop-up list will appear.
3. Type the keywords that you would like to search and click the Advanced Search button. You can search through all the words that you’ve typed, or you can narrow it down to specific words.
Research Skills
1. Critical Thinking
Critical thinking involves the ability to reflect on the information presented to you.
2. Data Organizing
As you collect the data, be sure to track where specific information is gathered.
3. Research Presenting
Part of your research is the actual writing, be creative and reflective in writing your search, explain every detail and step into achieving your objective.
Here are some tips in identifying good searches from satirical searches.
1. If the contents of the source are too impossible to happen, or too good to be true, then there must be something wrong.
2. If the site started as a false site for public figures such as TV personalities or political figures, then uploaded stories from different sources, it is a satirical one.
3. If the site is unfamiliar and continuously popping ads, then it is satirical.
Examples of Satirical News
1. The 2 years in K-12 Curriculum for Senior High School has been removed.
2. President Duterte resigned as the leader of the Philippine nation.
3. You can win 1 million pesos just by answering a given survey form.
4. A certain actress/actor is alleged as pregnant being in another country for a long time.
Sample satire news video: https://vt.tiktok.com/ZSRVV8STe/
Lesson 6: Applied Productivity Tools using Word Processor
A word processor is a computer program or device that provides for input, editing, formatting and output of text often with some additional features.
Early word processors were stand-alone devices often on its function, but current word processors are word processor programs running on general purpose computers.
Word Processor – Brief History
In the 1960s, a word processor was a stand-alone office machine with a keyboard, printer, electric typewriter, and a recording unit.
According to Harry Henderson, in his book titled ‘Encyclopedia of Computer Science and Technology‘, IBM (International Business Machine) is believed to have coined the term ‘word processor’ in the 1960s.
During the 1960s and 1970s, the features and designs gradually changed as technology advanced.
They had a monochrome (black and white) display, and were able to save documents on diskettes or memory cards.
The first ‘modern’ style word processor was brought to the market by Lexitron and Linolex.
It has a video display screen, so that the typist could see and correct errors without having to print it first.
By the late-1970s-early-1980s several innovations were introduced, including improved formatting options and spell-checkers.
In the late 1970s, word-processing systems developed by Wang, Data General, Digital Equipment Corporation, and others were essentially microcomputers with tiny monitors (screens), keyboards, printers and specialized software.
When personal computers, printers, and computer applications for word processing came onto the scene, sales of dedicated word processor machines plummeted/dropped.
In 2009, there were just two American companies – AlphaSmart and Classic – which continued making them.
Today, typical word processing software comprises more than one program and can produce a combination of graphics, images and text – with the text having type-setting capability.
Where are word processors used?
In the world of business, word processors are extremely common.
They are used for creating legal documents such contracts, company reports, literature for customers and clients, internal memos, and letters.
Some people use the software to write poems, short stories, personal correspondence, greeting cars, or to create résumés (CVs).
According to Top Ten Reviews, the top word processors (software) in the world are:
Microsoft Word (Microsoft Corporation – United States)
Word Perfect (Corel Corporation – Canada)
TextMaker (SoftMaker Software GmbH – Germany)
Google Docs (Google Inc. – United States))
Kingsoft Writer (Kingsoft 金山软件有限公司 – China))
Ability Write (Ability Software International – United Kingdom)
RagTime ((RagTime.de Development GmbH – Germany)
Microsoft Word Brief History
Microsoft word was released in 1983 as Multi-Tool Word.
Its first version was based on the framework of Bravo which was world's first graphical writing program.
Microsoft renamed Multi -Tool Word to Microsoft Word,
In October 1983, Microsoft released its first version for the IBM PC.
In 1989, Microsoft released a new version of Word for its Windows Operating Systems.
It was the Microsoft Word who introduced the concept of WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get).
In 2014, Microsoft developed the source code for Microsoft Word for Windows 1.1a.
Microsoft Word Parts and Uses
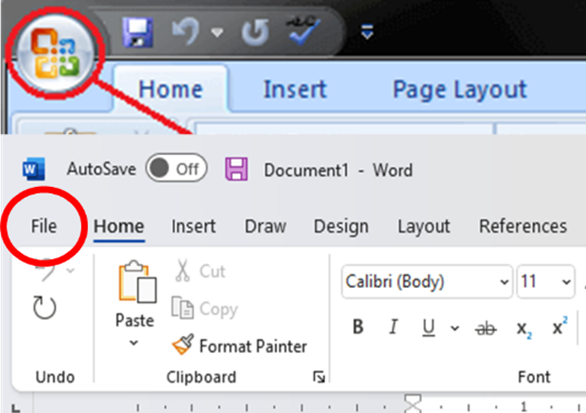
What is an Office Button/File Tab?
This button was introduced in Office 2007 with the new Ribbon feature.
When we click on the Office button, it displays some useful options which are used very frequently.
Office button/File Tab provides us options to open, save, print any document, or perform other common functions.
The following options or commands are displayed when we click on the Office button:
New: This option allows us to create a new, blank file in the corresponding Office program, such as MS Word, MS Excel, PowerPoint, etc. (shortcut key: Ctrl + N)
Open: This option allows us to open an existing file from the local storage on our computer. (shortcut key: Ctrl + O)
Save: This option allows us to permanently save a temporary file to our computer after finishing the work. (shortcut key: Ctrl + S)
Save As: This option allows us to save a copy of the active file with the desired file name and file extension to a desired location on the computer storage. (shortcut key: press F12)
Print: This option allows us to take a hard copy of the desired document on paper through a printer. (shortcut key: Ctrl + P)
Prepare: This option allows us to prepare the active file for distribution. In particular, the prepare option helps us view and modify the document properties accordingly.
Send: This option enables us to send or share the desired files directly through the opened Office program with others. In particular, we may share active documents by e-mail, upload them to OneDrive, or post to a specific blog.
Publish: This option enables us to distribute the desired document to people. We can even create a specific blog article with the content inside the file.
Close: This option helps us to close an active document in a corresponding Office program. (shortcut key: Alt + F4)
Title Bar
It displays the title of the currently open document or application.
Ribbon and Tabs
It is located below the Title Bar.
It comprises tabs; Home, Insert, Page layout, References, Mailing, Review and View.
Each tab has specific groups of related commands.
It gives you quick access to the commonly used commands that you need to complete a task.
Home tab:
The Home tab is the default tab in Microsoft Word.
It has five groups of related commands; Clipboard, Font, Paragraph, Styles and Editing.
It helps you change document settings like font size, adding bullets, adjusting styles and many other common features.
It also helps you to return to the home section of the document.
Insert tab:
Insert Tab is the second tab in the Ribbon.
As the name suggests, it is used to insert or add extra features in your document.
It is commonly used to add tables, pictures, clip art, shapes, page number, etc.
The Insert tab has seven groups of related commands; Pages, Tables, Illustrations, Links, Header & Footer, Text and Symbols.
Page Layout tab:
It is the third tab in the Ribbon.
This tab allows you to control the look and feel of your document, i.e. you can change the page size, margins, line spacing, indentation, documentation orientation, etc.
The Page Layout tab has five groups of related commands; Themes, Page Setup, Page Background, Paragraph and Arrange.
References tab:
It is the fourth tab in the Ribbon.
It allows you to enter document sources, citations, bibliography commands, etc.
It also offers commands to create a table of contents, an index, table of contents and table of authorities.
The References tab has six groups of related commands; Table of Contents, Footnotes, Citations & Bibliography, Captions, Index and Table of Authorities.
Mailings tab:
It is the fifth tab in the ribbon.
It is the least-often used tab of all the tabs available in the Ribbon.
It allows you merge emails, writing and inserting different fields, preview results and convert a file into a PDF format.
The Mailings tab has five groups of related commands; Create, Start Mail Merge, Write & Insert Fields, Preview Results and Finish.
Review tab:
It is the sixth tab in the Ribbon.
This tab offers you some important commands to modify your document.
It helps you proofread your content, to add or remove comments, track changes, etc.
The Review tab has six groups of related commands; Proofing, Comments, Tracking, Changes, Compare and Protect.
View tab:
The View tab is located next to the Review tab.
This tab allows you to switch between Single Page and Two Page views.
It also enables you to control various layout tools like boundaries, guides, rulers.
Its primary purpose is to offers you different ways to view your document.
The View tab has five groups of related commands; Document Views, Show/Hide, Zoom, Window and Macros.
LESSON 7: Advanced Word Processing Skills
I. Mail Merge and Label Generation
A. Mail Merge
Mail merge lets you create a batch of documents that are personalized for each recipient.
A feature that allows you to create documents and combine or merge them with another document or data file.
There are six steps in the mail merge wizard:
Under the Mailing Tab, click the dropdown of “Start Mail Merge and choose the Step-by-Step Mail Merge Wizard
1. Select the document type.
2. Start the document.
3. Select recipients.
4. Write your letter.
5. Preview your letters.
6. Complete the merge.
Two Components of Mail Merge
1. Form Document (Content of the Documents to be send)
The first component of our mail merged document is the form document. It is generally the document that contains the main body of the message we want to convey or send. The main body of the message is the part of the form document that remains the same no matter whom you send it to from among your list.
2. List or Data File (Address Book)
The second component of our mail merged document is the list or data file. This is where the individual information or data that needs to be plugged in (merged) to the form document is placed and maintained.
B. Label Generation
Included in the mail merge feature on Microsoft Word is the Label Generator.
It just makes sense that after you print out your form letters, you will need to send it to individual recipients in an envelope with the matching address printed directly on the envelope or on a mailing label to stick on.
All you need to do is select the correct or appropriate size for the label or envelope and select the data file that contains the addresses (data) to be printed.
II. Integrating Images and External Materials
Integrating or inserting pictures in your document is fun and it improves the impression of your document.
A. Kinds of Materials
1. Pictures
Generally, these are electronic or digital pictures or photographs you have saved in any local storage device.
There are three commonly used types of picture files (JPEG, PNG and GIF).
Pictures can be identified by the extension on their file names.
a. .JPG/JPEG
This is pronounced as “jay-peg“ and is the short form of .jpeg or Joint Photographic Experts Group.
Like all the rest of the image file extensions, it identifies the kind of data compression process that it uses to make it more compatible and portable through the Internet.
This type of image file can support 16.7 million colors that is why it is suitable for use when working with full color photographic images.
Unfortunately, it does not support transparency and therefore, images of this file type can be difficult to integrate in terms of blending with other materials or elements in your document.
This is pronounced as “jay-peg“ and is the short form of .jpeg or Joint Photographic Experts Group.
Like all the rest of the image file extensions, it identifies the kind of data compression process that it uses to make it more compatible and portable through the Internet.
This type of image file can support 16.7 million colors that is why it is suitable for use when working with full color photographic images.
Unfortunately, it does not support transparency and therefore, images of this file type can be difficult to integrate in terms of blending with other materials or elements in your document.
b. .GIF
This stands for Graphics Interchange Format.
This type of image file is capable of displaying transparencies.
Therefore, it is good for blending with other materials or elements in your document.
It is also capable of displaying simple animation.
Apparently, this may not be too useful on a printed document but if you are sending documents electronically or through email, or even post documents into a website, then this could be quite impressive.
c. .PNG
This is pronounced as “ping“. It stands for Portable Network Graphics.
It was built around the capabilities of .GIF. Its development was basically for the purpose of transporting images on the Internet at faster rates.
It is also good with transparencies but unlike .GIFs, it does not support animation but it can display up to 16 million colors, so image quality for this image file type is also remarkably improved.
2. Clip Art
This is generally a .GIF type; line art drawings or images used as generic representation for ideas and objects that you might want to integrate in your document.
3. Shapes
These are printable objects or materials that you can integrate in your document to enhance its appearance or allow you to have some tools to use for composing and representing ideas or messages. If you are designing the layout for a poster or other graphic material for advertising, you might find this useful.
4. Smart Art
These are predefined sets of different shapes grouped together to form ideas that are organizational or structural in nature. If you want to graphically represent an organization, process, relationships, or flow for infographic documents, then you will find this easy and handy to use.
5. Chart
This is quite useful when you are preparing reports that correlate and present data in a graphical manner.
6. Screenshot
Sometimes, creating reports or manuals for training or procedures will require the integration of a more realistic image of what you are discussing on your report or manual. Nothing can get you a more realistic image than a screenshot. (shortcut key: Windows Icon + PrtSc SysRq)
III. Image Placement
A. In Line with Text
This is the default setting for images that are inserted or integrated in your document. It treats your image like a text font with the bottom side totally aligned with the text line. This setting is usually used when you need to place your image at the beginning of a paragraph.
B. Square
This setting allows the image you inserted to be placed anywhere with the paragraph with the text going around the image in a square pattern like frame.
C. Tight
This is almost the same as the Square setting, but here the text “hug” or conforms to the general shape of the image. This allows you to get a more creative effect on your document.
D. Through
This setting allows the text on your document to flow even tighter taking the contours and shape of the image.
E. Top and Bottom
This setting pushes the texts away vertically to the top and/or the bottom of the image so that the image occupies a whole text line on its own.
F. Behind Text
This allows your image to be dragged and placed anywhere on your document but with all the texts floating in front of it. It effectively makes your image look like a background.
G. In Front of Text
As it suggests, this setting allows your image to be placed right on top of the text as if your image was dropped right on it. That means whatever part of the text you placed the image on, it will be covered by the image.
QUIZ#3
LESSON 8: Advanced Spreadsheet Skills
What is a Spreadsheet Software?
It allows users to organize data in rows and columns and perform calculations on the data
These rows and columns collectively are called worksheet.
Examples of Spreadsheet Software:
LibreOffice Calc
OpenOffice.org Calc
Google Sheets
Apple iWork Numbers
Kingsoft Office Spreadsheets
StarOffice Calc
Microsoft Excel
MICROSOFT EXCEL
Key Terms in MS Excel:
Row – horizontal line of entries in a table
Column – vertical line of entries in a table
Cell – the place where information is held in a spreadsheet
Active Cell – the selected cell
Column Heading – the box at the top of each column containing a letter
Row Heading – the row number
Cell Reference – the cell address of the cell usually combine letter and number (ex. A1, B4, C2)
Merge – combining or joining two or more cells
Formula – is an expression which calculates the value of a cell.
Functions – are predefined formulas and are already available in Excel
Formula Bar – the bar that displays the contents of a cell
FUNCTIONS
BASIC MATH OPERATIONS:
=SUM(x,y) or =SUM(range) – returns the sum of x and y or (all the numbers within the range)
=QUOTIENT(x,y) – returns the quotient of x divided by y
=x+y – returns the sum of x and y
=x*y – returns the product of x and y
=x/y – returns the quotient of x divided by y
=x-y – returns the difference of x subtracted by y
OTHER FUNCTIONS:
=ABS(x) – returns the absolute value of x
=AVERAGE(x,y) – returns the average of x and y
=CONCATENATE(x,y) – joins x and y
=IF(Condition, x, y) – returns x if the condition is true, else it returns y
=ISEVEN(x) – returns true if x is an even number
=ISODD(x) – returns true if x is an odd number
=COUNT(range) – counts the number of cell containing a number within a range
=COUNTIF(range, criteria) – count the number of cell that fits with the criteria within the range
=ISNUMBER(x) – returns true if x is a number
=ISTEXT(x) – returns true if x is a text
=LEN(x) – returns the length of characters in x
=PROPER(x) – returns the proper casing of x
=LEFT(x,y) – returns the characters of x specified by y (from the left)
=RIGHT(x,y) – returns the characters of x specified by y (from the right)
=PI() – returns the value of pi
=MIN(x,y) – returns the smallest number between x and y
=MAX(x,y) – returns the largest number between x and y
=MIN(range) – returns the smallest number within the range
=MAX(range) – returns the largest number within the range
=POWER(x,y) – returns the value of x raised to the power of y
=ROUND(x,y) – rounds x to a specified number of digits (y)
=COLUMN(x) – returns the column number of x
=ROW(x) – returns the row number of x
=SQRT(x) – returns the square root of x
=TRIM(x) – removes extra spaces in x
=UPPER(x) – returns x in all capital form
=LOWER(x) – returns x in non- capital form
=TODAY() – returns the current date
=NOW() – returns the current date and time
QUIZ#4
Quiz #4 Empowerment Technologies
Answer this 20-item online quiz. Follow the Instruction below:
1. Click the link below for Empowerment Technologies Facebook Page
2. Click the MESSAGE button
3. Type ONLINE QUIZ 1 then press send
4. Start answering the online quiz.
LESSON 9: Advanced Presentation Skills
Powerpoint
It is a highly innovative and versatile program that can ensure a successful communication whether you’re presenting in front of potential investors, a lecture theatre or simply in front of your colleagues.
The five features of powerpoint:
1. adding smart art
2. Inserting Shapes
3. Inserting an Image
a. .JPG/JPEG
b. .GIF
c. .PNG
4. Slide Transitions
5. Adding Animations
Creating an Effective Presentation
1. Minimize
Keep slides counts to a minimum to maintain a clear message and to keep the audience attentive.
Remember that the presentation is just a visual aid.
Most information should still come from the reporter.
2.Clarity
Avoid being to fancy by using font style that is easy to read.
Make sure that it is also big enough to be read by the audience.
Once you start making your presentation, consider how big the screen is during your report.
3.Simplicity
Use bullets or short sentences
Summarize the information on the screen to have your audience focus on what the speaker is saying than on reading the slide.
Limit the content to six lines and seven words per line.
This is known as the 6 x 7 rule.
4. Visual
Use graphics to help in your presentation but not too many to distract the audience.
In addition, instead of using table of data, use charts and graphs.
5. Consistency
Make your design uniform.
Avoid having different font styles and backgrounds.
6. Contrast
Use a light font on dark background or vice versa.
This is done so that it is easier to read.
In most instances, it is easier to read on screen if the background is dark.
This is due to the brightness of the screen.
Lesson 10: Imaging and Design for Online Environment
Creating a web page is like creating a work of art. There are certain things that you need to consider in order to get your message across.
Topic1. Basic principles of graphics and layout
1. Balance. It refers to the proper arrangement of the elements, which gives a visual weight for the design. There are two types of balance, Symmetrical or Asymmetrical. Symmetrical balance is where the elements are equally distributed on both sides of your design, technically a mirror-based design.
In contrast, Asymmetrical balance is a free layout where the elements can be placed in any order or the opposite of symmetrical.
2. Emphasis. Emphasis deals with the parts of a design that are meant to stand out. In most cases, this means the most important information the design is meant to convey.
When working on emphasis, you can change the color, size, or even the element itself to lead the eye to the focal interest.
3. Movement. Movement refers to the way the eye travels over a design. The most important element should lead to the next most important and so on. This is done through positioning (the eye naturally falls on certain areas of a design first), emphasis, and other design elements already mentioned.
4. Repetition. Repetition is a great way to reinforce an idea. It’s also a great way to unify a design that brings together a lot of different elements. Repetition can be done in a number of ways: via repeating the same colors, typefaces, shapes, or other elements of a design.
5. Rhythm. The spaces between repeating elements can cause a sense of rhythm to form, similar to the way the space between notes in a musical composition create a rhythm. There are five basic types of visual rhythm that designers can create: random, regular, alternating, flowing, and progressive.
Random rhythms have no discernable pattern. Regular rhythms follow the same spacing between each element with no variation. Alternating rhythms follow a set pattern that repeats, but there is variation between the actual elements. Flowing rhythms follow bends and curves, similar to the way sand dunes undulate or waves flow. Progressive rhythms change as they go along, with each change adding to the previous iterations.
Random rhythms
Regular rhythms
Alternating rhythms
Flowing rhythms
Progressive rhythms
Rhythms can be used to create a number of feelings. They can create excitement (particularly flowing and progressive rhythms) or create reassurance and consistency. It all depends on the way they are implemented.
6. Pattern. Patterns are nothing more than a repetition of multiple design elements working together. Wallpaper patterns are the most ubiquitous example of patterns that virtually everyone is familiar with.
7. Proportion. Proportion is one of the easier design principles to understand. Simply put, it’s the size of elements in relation to one another. Proportion signals what’s important in a design and what isn’t. Larger elements are more important, smaller elements less.
8. Variety. Variety in design is used to create visual interest. Without variety, a design can very quickly become monotonous, causing the user to lose interest. Variety can be created in a variety of ways, through color, typography, images, shapes, and virtually any other design element.
Infographics – is the combination of the words ‘information’ and ‘Graphics’, meaning, information from graphics. Graphics, pictures and images can convey a lot of information especially when it has context.
There is software that can be used in creating Infographics most requires advance knowledge and skills to make or needs internet connection to use.
Topic 2. Creating infographics
Creating infographics Using VistaCreate
1. In your Google Play Store download VistaCreate: Graphic Design
2. Once downloaded Open the application
3. Create an account
4. You can start making your infographics
5. Once done on the design, Download the final output using jpeg format.
Topic 3. Online file formats for images
Website images has a more compressed image because data travels over the internet and not everyone has a fast internet connection. Consequently, we have to use compressed images on our websites.
Here are the common image formats used on the wed:
1. Joint Photographics Experts Group (.jpeg or .jpg)
2. Graphics Interchange Format (.gif) supports transparency and animation
3. Portable Network Graphics (.png) supports transparency
Topic 4. Principles and basic techniques of image manipulation
Most of the time, we just capture an image and upload it as is on our Facebook account. From there, facebook does the rest by formatting our image to best fit the standards set by Facebook. But once you run your own website, you will have to edit your images.
Here are some tips to help you edit images for your website:
1. Choose the right file format. Knowing the purpose is the key to finding out the best file format.
2. Choose the right image size. Know how much space you want the image to consume. Or have a preview where the audience has the option to “see full size”.
3. Caption it. Remember to put a caption on images whenever possible.
Topic 4. Uploading, sharing and image hosting
Sharing your photo over the internet has never been so easy using social media. However, it is highly recommended to put your social media photos private and separated from the ones that are posted over the internet. In that case, you need an image host.
Image hosts are websites specializing in storing photographs.
Uploading and Photo sharing websites
Flickr
Picasa
PhotoBucket
Uploading and Video sharing websites
Youtube
Vimeo
Metacafe
Hulu
Vevo
Tiktok
Lesson 11: Online Platforms for ICT Content Development
We will focus on platforms that will allow us to share our own content to the rest of the world.
2 Types of Platforms
1. Social Media Platforms. Websites like Facebook allow you to create not only personal accounts but also pages and groups where you can share content. The only downside of this is that you are restricted to Facebooks one-size-fits-all design.
2. Blogging Platforms. Websites like Bloggers, WordPress, and Tumblr focus on content and design. It typically looks like a newsletter where you are given options to change the design to your liking.
Example on how to use Blogger Mobile App: https://vt.tiktok.com/ZSNfP8UqQ/
Performance Task#1 Final Term
Creating Your PERSONAL BLOG using BLOGGER.COM
Lesson 12: Basic Web Page Creation
WYSIWYG is the acronym for What You See Is What You Get. This means that whatever you type, insert, draw, place, rearrange, and everything you do on a page is what the audience will see.
Creating a website using Microsoft Word
1. Open a Microsoft Word
2. Type the blog that you make in the previous lesson
3. Press F12
4. Specify the Filename “Your Complete Name”
5. On the Save As Type, select “Web Page (*.htm; *html).”
6. Click the Change Title Button
7. Input the title of the blog, then click OK then Save.
8. Open the blog you created.
Example on how to Convert Microsoft Word to Web Page: https://vt.tiktok.com/ZSNfPtGdV/
Lesson 13. Collaborative ICT Development
Web Portals. A web portal is a website that contains information from different sources and places in one location in a uniform way. An example of a web portal is a yahoo and bing.
Websites that offer a web portal where news, email, weather, etc. are found in one page.
Online Collaborative Tools
Working together does not necessarily mean you have to be physically together. These tools can help your group “go the distance” and work as if you already have your own office.
There are plenty of online collaborative tools:
1. Facebook Groups to create a group page that will allow people in your group to communicate your ideas.
2. WordPress also allows you to multiple contributors for a single blog.
3. Google Drive allows multiple people to work on different office files and even have their own groups cloud storage.
Lesson 14. Interactive Multimedia
Multimedia Content
Here are multimedia contents that you can find on some websites:
1. Videos
2. Sound, Music or Audio
3. Online Games
4. Online Test – online test that automatically display the results when finished
5. Courseware – online courses that simulates the classroom online
6. Podcast – audio or text files streamed online
7. Vodcast – video streamed online
Lesson 15. ICT as Platform for Change
Information Communications Technology has the power to transform society.
What is Advocacy?
Advocacy means giving a person support to have their voice heard.
It is a service aimed at helping people understand their rights and express their views.
The Power of Social Media
The true power of social media is influence.
Social provides an avenue for companies to not only engage with customers, but also influence them with the right content that helps them make a decision.
What Is Digital Citizenship?
Digital Citizenship refers to the ability to engage positively, critically and competently in the digital environment, drawing on the skills of effective communication and creation, to practice forms of social participation that are respectful of human rights and dignity through the responsible use of technology.
What is the Digital Divide?
Digital Divide refers to the growing gap between the underprivileged members of society, especially the poor, rural, elderly, and handicapped portion of the population who do not have access to computers or the internet; and the wealthy living in urban areas who have access.
The Role of ICT in Recent History
1. EDSA (People Power Revolution) – To end the regime of then President Ferdinand Marcos Sr. A major protest took place along EDSA from February 22-25, 1986 involving 2 million Filipinos from different sectors. The radio broadcast helped change the course of history.
2. EDSA Dos – Also known as 2001 EDSA Revolution, happened during January 17 to 21, 2001. EDSA Dos would not have been successful without the text brigades.
3. Million People March – Took place in Luneta Park from August 22 to 26, 2013. It was to condemn the misuse of the Priority Development Assistance Fund (PDAF). The organizers and promoters of the Million People March used Facebook and Change.org as their mediums.
4. Yolanda People Finder – Recent storms in Philippines history gave birth to the People Finder database powered by google. People Finder was a vital tool for people across the globe to track the situation of their loved ones and relatives.
Change.org – is dubbed as the “worlds platform for change” where anyone from the online community can create a petition and ask other to sign it. Its mission is to help people around the world create the change they want to see.
Example on how to use change.org: https://vt.tiktok.com/ZSNfPfoCK/
Lesson 16. ICT Project for Social Change
Social Change – refers to an alteration in the social order of a society. Social Change may include social institutions, social behaviors, or social relations. It can be done in any form of multi-media.
Simplified ICT Project Process Overview:
Planning —> Development —> Release and Promotion —> Maintenance
1. Planning – involves the following task (but not limited to):
• Conceptualizing your project project
• Researching on available data about your topic
• Setting deadlines and meetings
• Assigning people to various tasks
• Finding a web or blog host
• Creating a site map for tour website
• Listing down all applications, that you need including web apps
• Funding (If applicable)
Creating a Concept Paper
Before starting your project, your group should be able to do the necessary paperwork. This allows experts to see if your project is doable over the time frame that was given and if it is significant enough to be made into reality.
A concept paper is a document used to convince a panel of potential funders to help a product, program, or service to become a reality.
There are five elements of a concept paper:
1. Introduction - includes tour group’s mission and vision and a brief introduction of your project.
2. Purpose- includes the reasons why this project is worth your group and your sponsor’s time, effort and money.
3. Description - includes all the necessary information about the project. In ICT, it involves the sites you are going to produce and the purpose of each and how they work in unison.
4. Support - contains the budget needed for the project. Some concept papers do not specify any amount requested from the sponsor.
5. Contact information - includes information on how the group be contacted.
Sample Concept Paper
Project Title: Social Media Awareness on Cyberbullying
Introduction
Cyberbullying is a serious problem that affects millions of children and young adults around the world. It is the use of electronic communication to bully a person, typically by sending messages of an intimidating or threatening nature. Social media is a common platform for cyberbullying, as it allows bullies to target their victims anonymously and in front of a large audience.
Our group is committed to raising awareness of cyberbullying and helping to prevent it. Our vision is to create a world where all young people can use social media safely and respectfully. Our mission is to educate and empower young people to stand up to cyberbullying and create a more positive online community.
Purpose
This project is worth our time, effort, and money because it has the potential to make a real difference in the lives of young people. Cyberbullying can have a devastating impact on victims, leading to anxiety, depression, and even suicide. By raising awareness of cyberbullying and teaching young people how to prevent and respond to it, we can help to create a safer and more supportive online environment.
Description
Our project will involve creating a series of social media awareness campaigns on cyberbullying. We will develop educational content, such as infographics, videos, and blog posts, that will teach young people about cyberbullying, how to identify it, and how to respond to it. We will also create a social media community where young people can come together to support each other and share resources.
Our social media awareness campaigns will be targeted at young people between the ages of 12 and 18. We will use a variety of social media platforms, including Instagram, TikTok, and Snapchat, to reach our target audience.
Support
The budget for this project is estimated to be Php10,000. This money will be used to cover the costs of developing our educational content, promoting our social media campaigns, and maintaining our social media community.
Contact Information
Should you have any questions about our project feel free to contact us at emtech@gmail.com.
Conclusion
Our social media awareness campaigns will work in unison to create a comprehensive educational experience for young people. Our infographics, videos, and blog posts will provide young people with the information they need to understand cyberbullying and how to prevent it. Our social media community will provide a safe and supportive space for young people to share their experiences and get help if they are being bullied.
We believe that our social media awareness campaigns will make a real difference in the fight against cyberbullying. By educating and empowering young people, we can help to create a safer and more supportive online environment for everyone.
2. Development – involves the actual creation of the website(s), involves the production of images, infographics, etc.
Medias you can use:
Text
Videos
Pictures
Audio
Websites
3. Release and Promotion – involves the actual release of the website for public view and promoting it. Promotion typically starts before the actual release.
4. Maintenance – involves responding to feedback of your site visitors and continuing to improve your website.
Lesson 17: ICT Project Publication and Statistics
Website operators use website statistics to determine their visitors demographic and the time and day they usually log in. These statistics are used to know when a site owner should publish new content and which determine which content could affect more visitors.
Lesson 18: ICT Project Maintenance
User Feedback – is an essential way of improving your website. It allows your sites visitors to have their say about the sites strength and weaknesses.
Google Forms allows your audience to answer a set of questions you have set which can then be imported as a part of a spreadsheet and later used in a chart.
Lesson 19: The Disadvantage of ICT
Cybercrimes are illegal acts done through the use of the Internet.
In 2012, Stephen Nale (Complex.com) posted a list of ten most common Internet cybercrimes as follows:
1. Phishing/Spoofing - the act of sending multiple emails to multiple users in hopes of having a number of them clicking on the links or malwares attached to the email. Most email services today have spam or bulk folders that automatically put these suspicious emails to that folder. However, this is not 100% accurate that some emails are not filtered and some other emails that are legitimate end up on the spam folder.
2. Blackmail/Extortion - the act of using the Internet to threaten or damage someone's reputation to extort money or anything else of value. This can be avoided if you are aware of what you should post on the Internet. The victims of this act tend to have posted something "inappropriate" over the Internet even if they put it at a secured location.
3. Accessing Stored Communications or hacking; the act of obtaining unauthorized access to data from a computer network. This is typically done to commercial and government sites to threaten its owner. In late 2014, a group of hackers hacked Sony's website because of the impending release of the controversial film "The Interview."
4. Sports Betting - the act of wagering on any sports event over the Internet. In some countries, gambling (including sports betting) is illegal even if you are doing it over the Internet.
5. Non-Delivery of Merchandise - the act of devising a scheme wherein a culprit. posts an item or service for sale on the Internet and once the transactions have been done, does not really give the item or service.
6. Electronic Harassment - the act of anonymously using the Internet to harass, abuse, threaten, or annoy other people. This is also an act of cyberbullying, however, because the culprit is anonymous, it is hard to detect who is bullying you.
7. Child Pornography - the act of using the Internet to show child pornography. This act is highly punishable by law.
8. Prostitution - the act of using the Internet to engage in prostitution
9. Drug Trafficking - the act of selling illegal substances using the Internet
10. Criminal Copyright Infringement - the act of piracy mainly for financial gain. In late 2014, the number one pirate website, ThePirateBay, was raided for the second time due to years of pirating movies, music, games, books, and other software. These kinds of websites earn money through advertising.
The Internet is the present and the future of your generation and you define what impact it can do to shape our society, whether it is negative or positive. The future is in your hands.
Combatting Cybercrimes
There are several ways the authorities can help solve or prevent cybercrimes. Here are some of them:
1. Network Security. Before a hacker can get through the unauthorized files he or she is targeting, the hacker has to get through several security measures like firewalls, secure connections, passwords, anti-malwares, and data encryptions. Encryption is the process of converting raw data into code. However, these methods are not 100% secure and there will always be a way for a hacker to hack.
2. Investigation. URL tracing and logging are used by websites to track your unique IP addresses. This can be used by investigators to trace hackers. In piracy, trackers are used to identify IP addresses currently sharing a pirated file.
3. Penalties. More and more laws are being created and implemented today. Penalties include both a fine and imprisonment.
FINAL EXAMINATION
Click the link below for the ONLINE FINAL Examination in Empowerment Technologies.
Goodluck!
https://m.me/LecturesWithSirO?ref=w21793993
Facebook messenger po ang gagamitin bawal ang fb lite.
Then Click Get started.
References:
Yuvienco, Joel C. “Empowerment Technologies Student Reader”. Department of Education-Bureau of Learning Resources (DepEd-BLR)
Curriculum Guide SHS-Applied_Empowerment-Technologies-for-the-Strand
RBS Empowerment Technologies First Edition. Rex Book Store, Inc. and Innovative Training Works, Inc. June 2016
WRITER/EVALUATOR: ROMMEL M. MAGCALAS is a graduate of Bataan Peninsula State University with the degree of Bachelor of Science in Electronics Engineering, year 2011. At age 21 he started working in a Manufacturing Company in Olongapo City as Engineer 1 who leads his automation team in Nidec Subic Philippines. After 2 years and 8 months he decided his luck abroad, and work as a Technical Specialist in Iqor Malaysia for almost 2 years. He taught for 2 years and 3 months in the University of Nueva Caceres – Bataan a private school located at Rizal St. Dinalupihan, Bataan teaching Calculus and Physics Subjects to STEM Strand Students in the year 2017-2019. In 2019 he successfully passed the Civil Service Examination. He finished his Professional Teaching Certificate gaining 24 units at College of Most Holy Trinity Catholic Foundation, Incorporated, in 2020. He also successfully passed the Licensure Examination for Teachers (LET) in 2022. From 2019-2024 he work at St. Francis National High School, teaching Senior High School students, also a Learning Resource Coordinator and School Librarian. At present, he work at Pagalanggang National High School, teaching Senior High School students.































































































Comments
Post a Comment